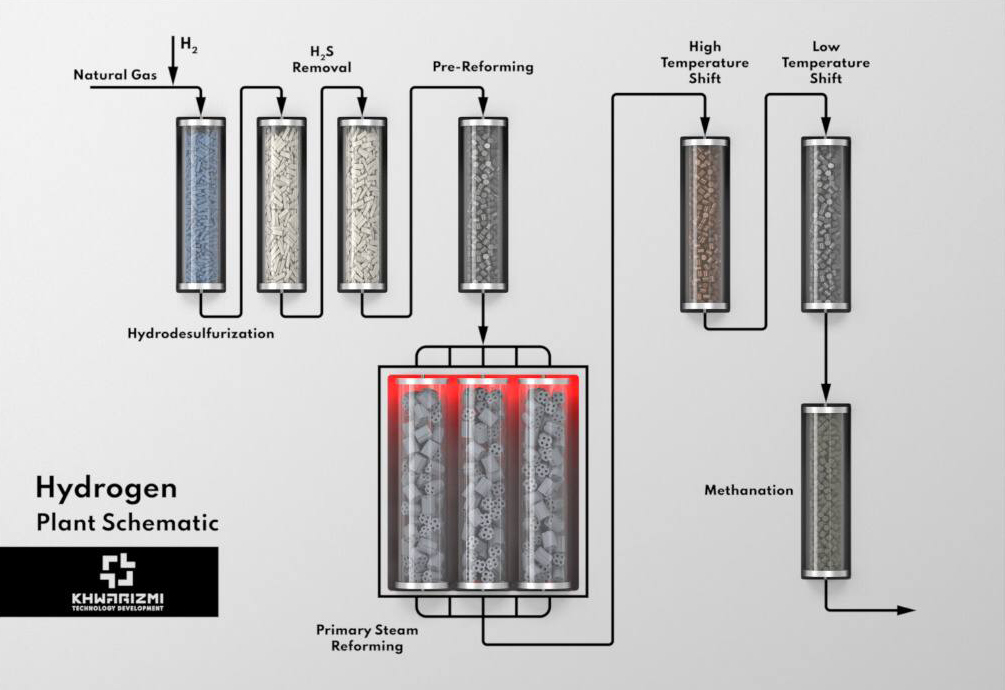
Hydrogen is an essential raw material for every refinery and chemical plant. It is primarily used in methanol, ammonia and DRI production plants (not as a pure stream) followed by refinery plants for hydro-treatment of hydrocarbons as well as hydrogenation of unsaturated or aromatic hydrocarbons. The pure stream of this compound is produced in hydrogen plants and refineries, which further can be used in downstream reactors or units. In industrial plants, hydrogen is produced mainly from steam reforming of light hydrocarbons over nickel based catalysts.
Prior to syngas production in a steam reformer, natural gas has to be free of contaminations which have the adverse effect catalysts. Natural gas typically contains different levels of sulfur compounds, in the form of hydrogen sulfide and/or organic sulfur containing components which are highly poisonous to the downstream catalysts and must be removed. The organic sulfur containing materials is hydrogenated in HDS units and hydrogen sulfide is adsorbed in the next vessels utilizing zinc oxide sulfur removal adsorbents.