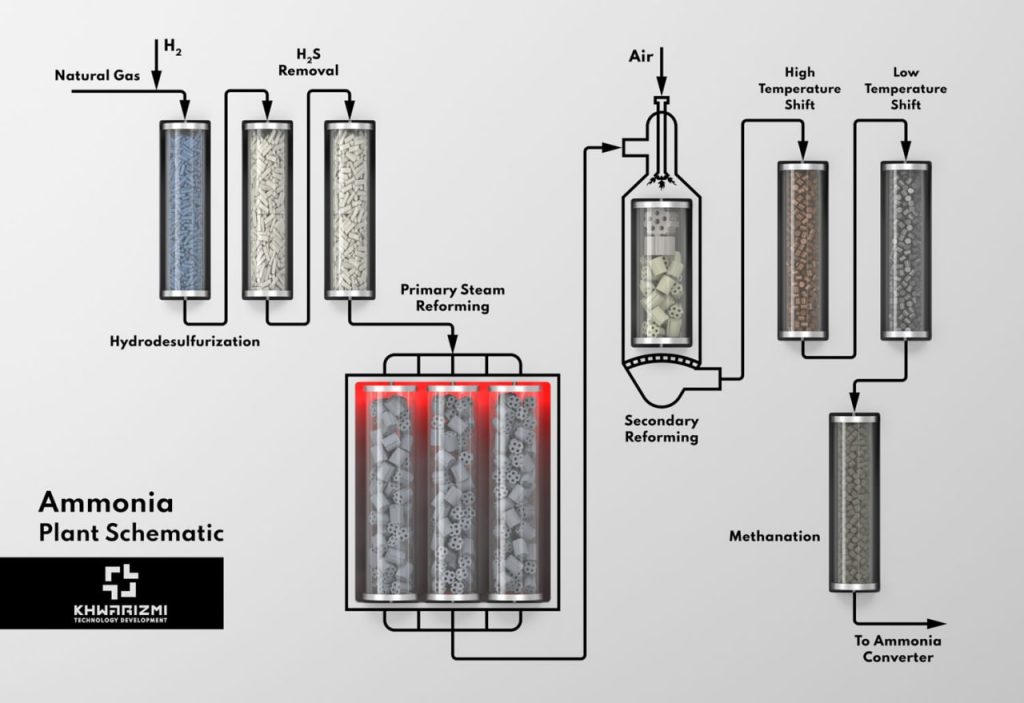
Ammonia is one of the most vital chemicals for the industrial applications especially for agricultural industry. The manufacture of fertilizers is by far the most important use of ammonia in the world. It is being increasingly produced in countries which have low cost sources of natural gas. In the process of ammonia synthesis in petrochemical plants, in the first step, it is necessary to produce hydrogen from natural gas. The manufacture of hydrogen involves several distinct processes.
At first, syngas from natural gas is produced using typical reforming process and subsequently, carbon monoxide will be converted into hydrogen using water gas shift reactors. Prior to syngas production, natural gas has to be free of contaminations which have adverse effect on the downstream catalysts. Natural gas typically contains different levels of sulfur compounds, in the form of hydrogen sulfide and/or organic sulfur containing components which are highly poisonous to the downstream catalysts and must be removed.